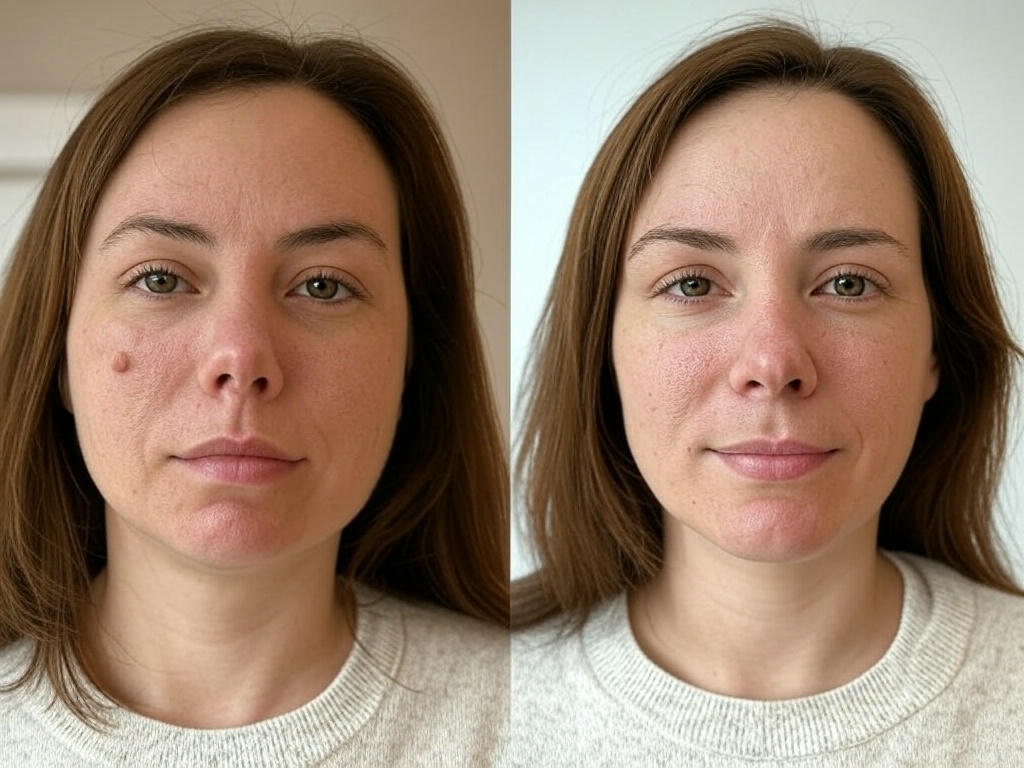
Why Your Moisturizer Isn’t Enough for Dry Hands
Many people rely on moisturizers to keep their skin soft, applying them repeatedly to their hands and face. However, by the next day, the effects disappear, requiring constant replication. What most don’t realize is that many moisturizers contain alcohol, a substance that dehydrates the skin rather than nourishing it. When lotions are absorbed, their ingredients enter the bloodstream and ultimately reach the liver, which is something to consider when choosing skincare products.

Natural Alternatives for Hydrating Dry Hands
There are plenty of natural options available that can help keep skin moisturized. Common choices include vitamin E, coconut oil, and tallow. However, today’s focus is on a unique compound that plays a key role in skin health: hyaluronic acid.
What is Hyaluronic Acid and How It Works
Hyaluronic acid is naturally produced by the body and is present in various tissues, including the skin and joints. Its most remarkable property is its ability to hold up to 1,000 times its weight in water, making it a powerful hydrator. Picture a thin, invisible wetsuit covering your body—that’s how hyaluronic acid functions in your skin. It resides in the deeper layers, keeping skin looking youthful and aiding in wound healing and sunburn recovery. Its production is also influenced by vitamin A, which explains why deficiencies in this vitamin can lead to dry skin and even dry eyes.
How Aging Affects Hyaluronic Acid Levels in Skin
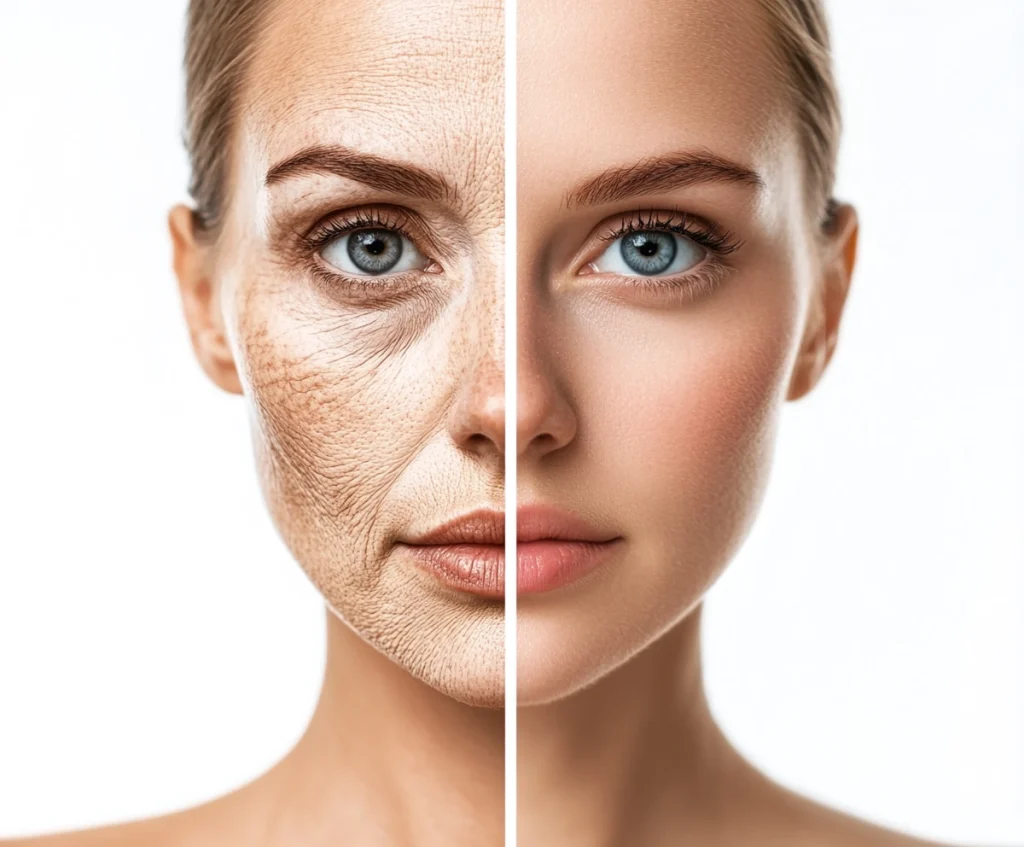
As people age, their natural levels of hyaluronic acid decline significantly. By the time someone reaches 40–50 years old, these levels have already dropped, and by 80 years old, about 80% of it is gone. A rare condition called progeria demonstrates the importance of hyaluronic acid, as individuals with this disorder lose it at 20 times the normal rate, leading to premature aging.
If you compare youthful, plump skin to older, more wrinkled skin, the difference is often due to this loss of hyaluronic acid.

Ways to Replenish Hyaluronic Acid for Healthier Hands
There are several ways people attempt to restore hyaluronic acid in their skin:
- Injections – Some clinics offer direct injections into the skin for a more immediate effect.
- Topical Application – Many skincare products contain hyaluronic acid, but they must be alcohol-free to be effective.
- Oral Supplements – Although some believe it cannot be absorbed, research shows that around 2.5% of consumed hyaluronic acid is absorbed by the body—enough to help replenish lost stores over time.

The Secret to Longevity: Hyaluronic Acid in Japanese Diet
A fascinating study by journalist Connie Chung explored a village in Japan where many residents lived well past 100 years old while remaining active. Their longevity was attributed to their diet, particularly the consumption of a root vegetable naturally rich in hyaluronic acid.
For reference, a 45-year-old typically has 14–15 grams of hyaluronic acid in their body. By 80 years old, this amount drops to around 3.6 grams. Given this decline, supplementing with hyaluronic acid could be beneficial for maintaining skin elasticity and joint health.
Dosage Guide and a Cautionary Tale
While supplementation can be helpful, more is not always better. A friend of mine once decided to take an extreme approach, consuming 3,000–4,000 mg per day. Since hyaluronic acid holds water, this excess caused serious swelling issues. In his case, he ended up drinking straight brandy to counteract the effects and dissolve some of the excess buildup—definitely not a recommended strategy!
For a safe and effective approach, 200 mg per day is a reasonable dose for most people.

Maximizing the Benefits of Hyaluronic Acid for Your Hands
For best results, follow these steps:
- Topical Application – Make sure your hands are damp before applying. Use only a few drops, rub them together, and distribute evenly over your hands.
- Facial Hydration – A similar method works for the face. Apply a small amount to slightly moistened skin for better absorption.
- Diet and Internal Health – Skincare is not just about what you put on your skin; nutrition plays a huge role. A diet rich in essential nutrients, such as a healthy ketogenic diet, helps support internal hydration and collagen production.